Keeping Linux updated ensures security patches, bug fixes, and performance improvements. Here’s how to update safely on Ubuntu/Debian and CentOS/AlmaLinux.
Before starting make sure ur linux is ready.
- Ubuntu: ubuntu.com/download
- Debian: debian.org/distrib
- CentOS Stream: centos.org/download
- AlmaLinux: almalinux.org/download
- Talkecho full toturial: Click here
Why Regular Updates Matter
- Security: Fix vulnerabilities quickly.
- Stability: Prevent crashes and bugs.
- Features: Get new software and kernel improvements.
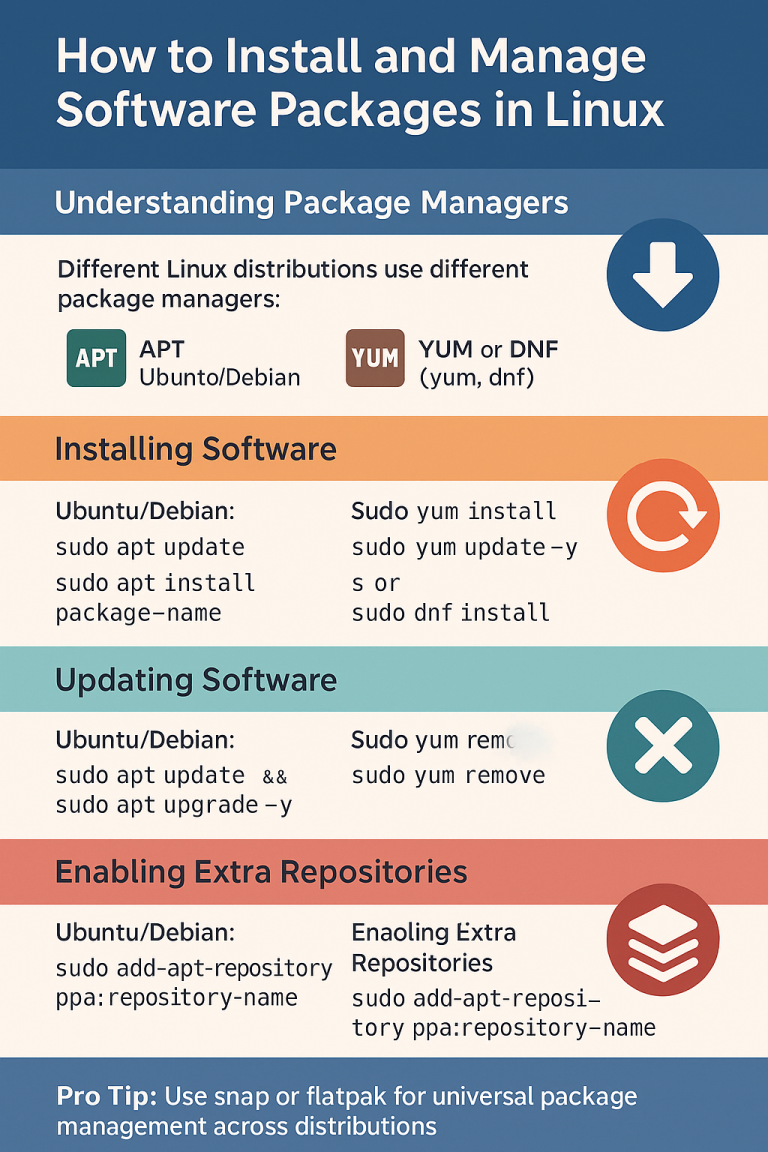
Updating on Ubuntu & Debian
# refresh package lists
sudo apt update
# upgrade all packages
sudo apt upgrade -y
# full upgrade (handles dependencies and kernel upgrades)
sudo apt full-upgrade -y
# remove unused packages
sudo apt autoremove -y
Tip: Use apt full-upgrade occasionally to keep your kernel and dependencies aligned.
Updating on CentOS & AlmaLinux
# update all packages
sudo dnf upgrade -y
# clean cache
sudo dnf clean all
# check for kernel updates
sudo dnf list kernel
Tip: After a kernel update, reboot to load the new version:
sudo rebootCheck Current Kernel Version
uname -rThis command shows the active kernel. After a reboot, it should match the latest installed version.
Best Practices
- Update regularly (once a week is recommended).
- Always reboot after kernel or system updates.
- Avoid interrupting updates; it can break packages.
- Back up important data before large upgrades.