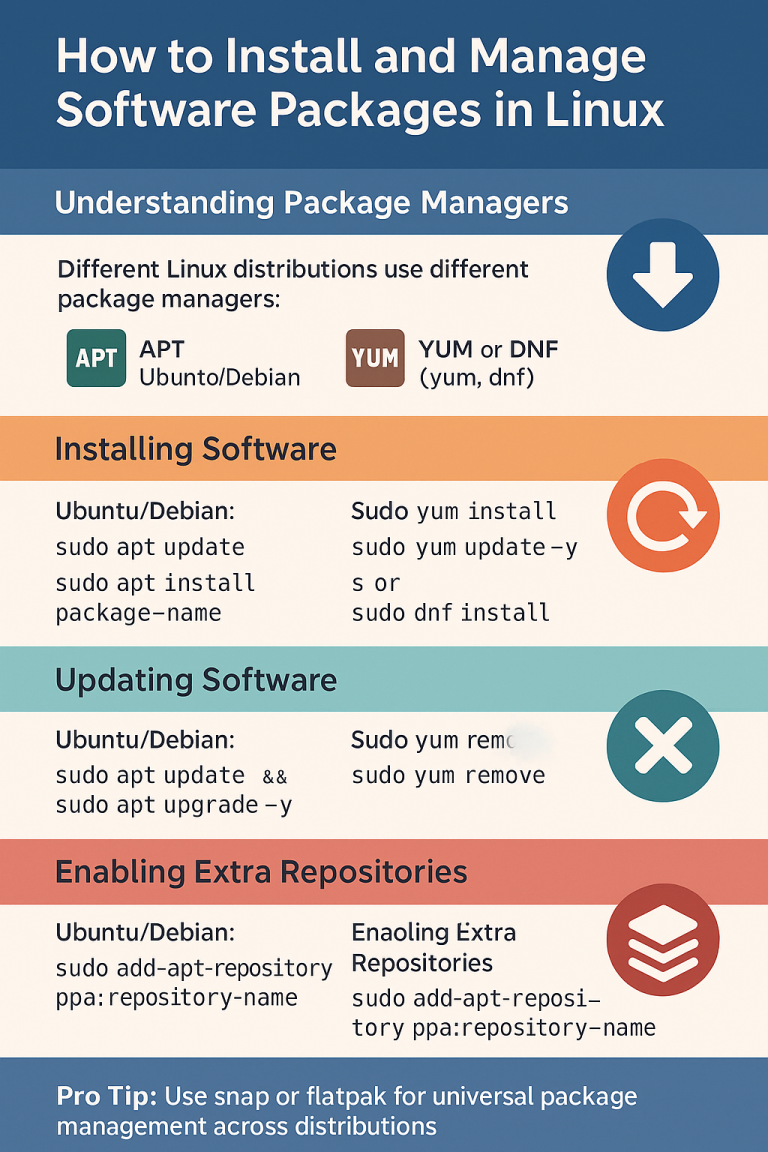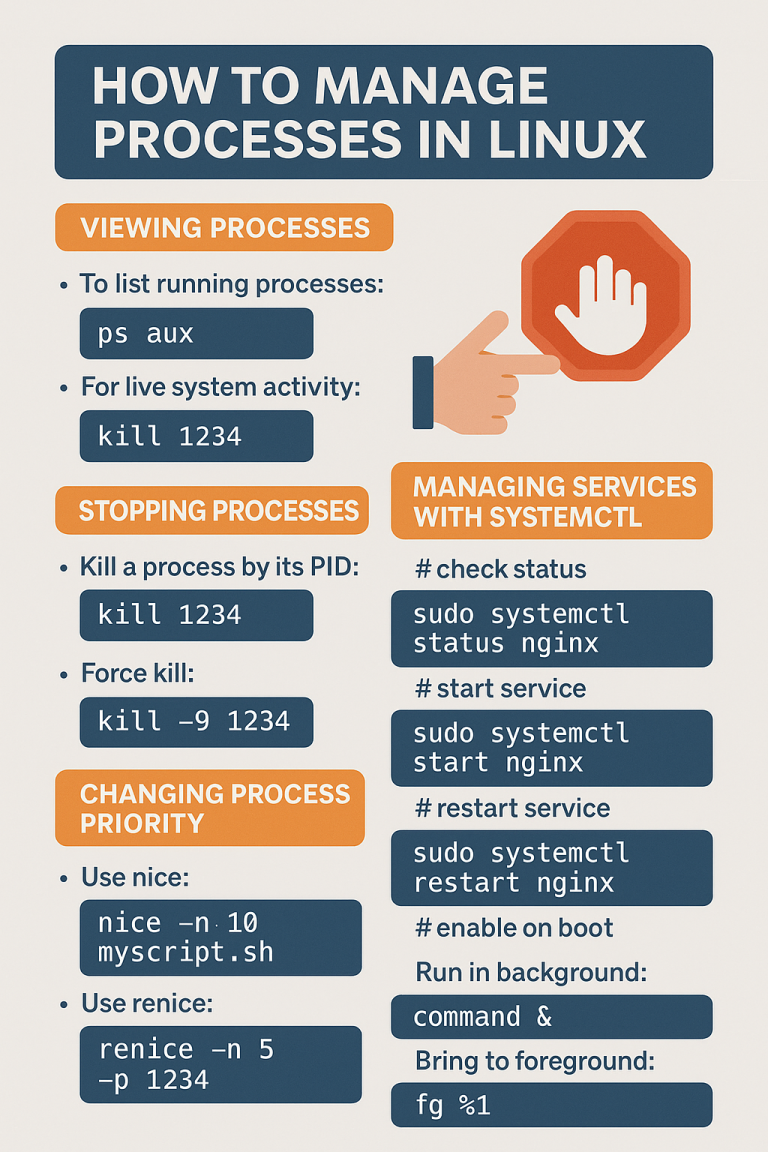
Learn how to set IP addresses, configure DNS, and manage network connections in Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and AlmaLinux.
Before starting make sure ur linux is ready.
- Ubuntu: ubuntu.com/download
- Debian: debian.org/distrib
- CentOS Stream: centos.org/download
- AlmaLinux: almalinux.org/download
- Talkecho full toturial: Click here
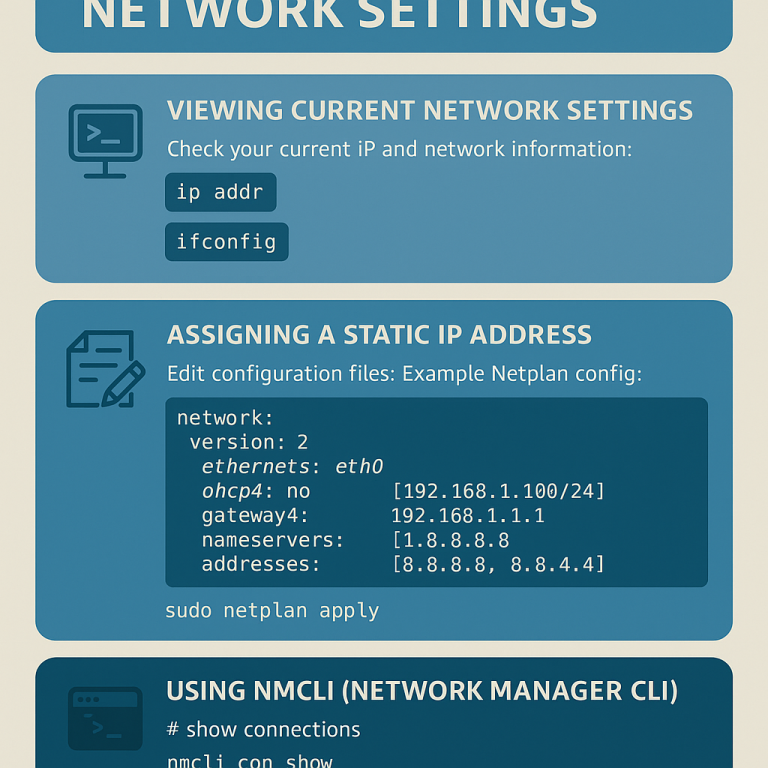
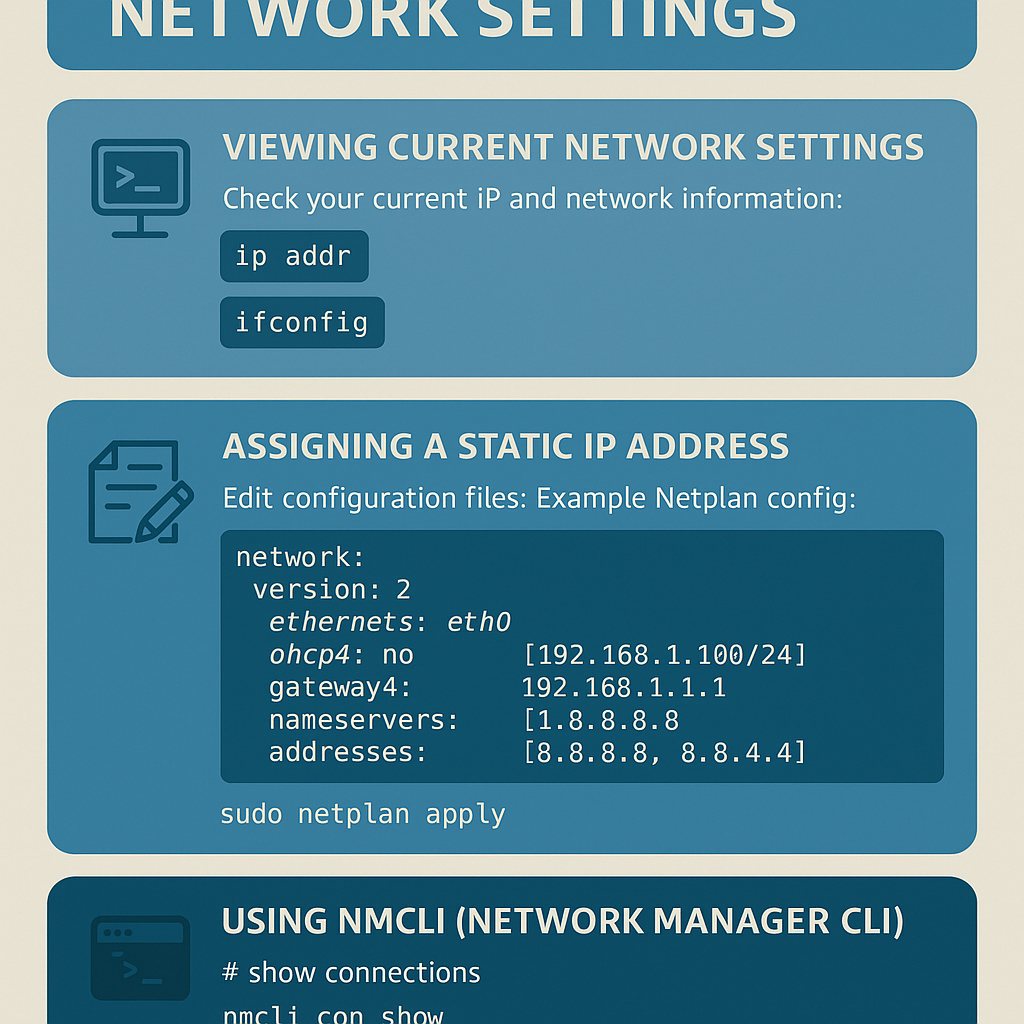
Viewing Current Network Settings
Check your current IP and network information:
ip addror:
ifconfig(Install net-tools if ifconfig is missing: sudo apt install net-tools on Ubuntu/Debian or sudo yum install net-tools on CentOS/AlmaLinux.)
Assigning a Static IP Address
Edit your network configuration files:
- Ubuntu/Debian (Netplan):
/etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml - CentOS/AlmaLinux:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Example Netplan config for static IP:
network:
version: 2
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.100/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]
Apply changes:
sudo netplan applyConfiguring DNS
To set custom DNS servers temporarily, edit /etc/resolv.conf:
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 1.1.1.1
For persistent changes, configure them in your network manager or Netplan/ifcfg files.
Using nmcli (Network Manager CLI)
# show connections
nmcli con show
# add static IP
nmcli con mod "Wired connection 1" ipv4.addresses 192.168.1.200/24
nmcli con mod "Wired connection 1" ipv4.gateway 192.168.1.1
nmcli con mod "Wired connection 1" ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8 1.1.1.1"
nmcli con mod "Wired connection 1" ipv4.method manual
nmcli con up "Wired connection 1"