Learn how to view and manage network interfaces, IP addresses, and connections on Linux using ifconfig, ip, and netstat.
Before starting make sure ur linux is ready.
- Ubuntu: ubuntu.com/download
- Debian: debian.org/distrib
- CentOS Stream: centos.org/download
- AlmaLinux: almalinux.org/download
- Talkecho full toturial: Click here
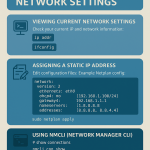
Checking Network Interfaces with ifconfig
ifconfig is part of the net-tools package (deprecated but still common).
# install net-tools if missing
sudo apt install net-tools # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo dnf install net-tools # CentOS/AlmaLinux
# show all network interfaces
ifconfig -a
# bring interface up or down
sudo ifconfig eth0 up
sudo ifconfig eth0 down
Using the ip Command (Modern Replacement)
The ip command (from iproute2) is the modern tool for networking.
# show all interfaces and IP addresses
ip a
# show routing table
ip route
# assign a new IP temporarily
sudo ip addr add 192.168.1.50/24 dev eth0
# remove assigned IP
sudo ip addr del 192.168.1.50/24 dev eth0
# bring interface up/down
sudo ip link set eth0 up
sudo ip link set eth0 down
Monitoring Connections with netstat
netstat shows open ports, routing, and connections.
# show all listening ports
netstat -tuln
# show active connections
netstat -antp
# show routing table
netstat -r
On newer systems, use ss as a faster replacement:
# show all listening sockets
ss -tuln
# show active TCP connections
ss -ant
Testing Connectivity
# ping an address
ping -c 4 google.com
# traceroute to a host
traceroute 8.8.8.8 # may need: sudo apt install traceroute
# check DNS resolution
dig example.com
host example.com
Best Practices
- Use
ipinstead ofifconfigfor modern setups. - Prefer
ssovernetstatfor better performance. - Make network config persistent by editing:
- Ubuntu/Debian:
/etc/netplan/ - CentOS/AlmaLinux:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
- Ubuntu/Debian: