Track CPU, memory, disk, and I/O usage in real time. This guide covers built-ins and popular tools on Ubuntu/Debian and CentOS/AlmaLinux.
Before starting make sure ur linux is ready.
- Ubuntu: ubuntu.com/download
- Debian: debian.org/distrib
- CentOS Stream: centos.org/download
- AlmaLinux: almalinux.org/download
- Talkecho full toturial: Click here
Quick Health Snapshot
# uptime, load averages, logged-in users
uptime
# memory usage (human readable)
free -h
# disk usage by filesystem
df -h
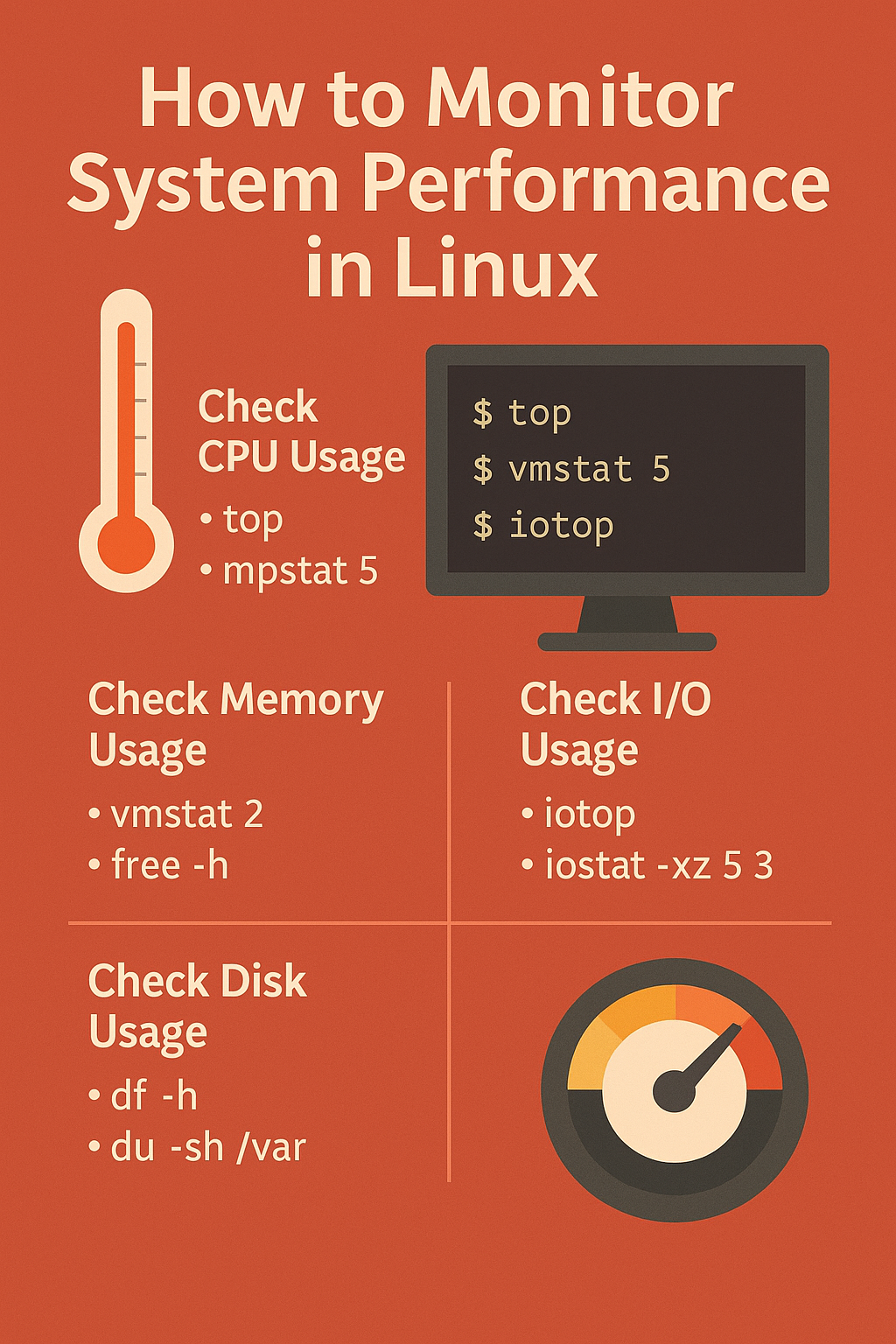
CPU Usage
# interactive overview
top
# improved interface (install first)
sudo apt install -y htop || sudo dnf install -y htop
htop
# per-core stats every 2s (sysstat package)
# Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt install -y sysstat
# CentOS/AlmaLinux:
sudo dnf install -y sysstat
mpstat -P ALL 2
Tip: In top/htop, press P to sort by CPU.
Memory & Swap
# processes + memory over time
vmstat 2 10
# who is using swap?
grep -H 'VmSwap' /proc/*/status 2>/dev/null | sed 's/\/proc\///;s/\/status:/ /' | head
Tip: High swap use with low RAM free indicates memory pressure.
Disk I/O (Reads/Writes)
# top-like view of I/O per process
sudo apt install -y iotop || sudo dnf install -y iotop
sudo iotop
# device throughput and latency
iostat -xz 5 3 # from sysstat
Watch for high await/svctm and busy (%util) disks.
Filesystem Usage & Heavy Folders
# usage by mount
df -h
# biggest directories (top 20) under /
sudo du -xh / | sort -h | tail -n 20
# focused scan (fast)
sudo du -xh /var | sort -h | tail -n 20
Network Throughput
# quick interface stats
ip -s link
# per-connection overview (modern replacement for netstat)
ss -tulpn
System Logs & Alerts
# live systemd journal
sudo journalctl -f
# kernel only
sudo journalctl -k -f
Investigate services that spike CPU/I/O using journalctl -u <service>.
Create a Baseline & Automate Checks
- Record normal ranges for load, memory, and disk I/O.
- Schedule a daily report:
cat <<'SH' | sudo tee /usr/local/bin/sys-health.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo "=== $(date) ==="
uptime
free -h
df -h
iostat -xz 1 2 | tail -n +4
SH
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/sys-health.sh
(crontab -l; echo "0 8 * * * /usr/local/bin/sys-health.sh >> ~/sys-health.log") | crontab -